Peripheral neuropathy, especially in the legs and feet, is a common but often misunderstood condition.
It can cause a range of uncomfortable symptoms like numbness, tingling, burning, or sharp shooting pain.
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure, many people find meaningful relief through a combination of home remedies and lifestyle adjustments.
In this post, we’ll break down the causes, symptoms, and evidence-based home treatments to help manage and reduce nerve pain.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy results from damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for sending signals between your central nervous system and limbs.
This damage can be caused by numerous factors including:
-
Diabetes
-
Aging
-
Thyroid disorders
-
Alcohol use
-
Smoking
-
Certain medications
-
Chemotherapy
-
Poor footwear or prolonged foot stress
The nerves in your toes and feet are particularly vulnerable because they are farthest from your spine and brain.
These nerves are long, thin, and more prone to injury or degeneration.
True nerve pain often worsens at night or while resting, whereas biomechanical pain (from muscle or joint issues) typically hurts during activity or when getting up in the morning.
Myths vs. Facts: Treatment vs. Cure
There are many products and supplements that promise to "cure" neuropathy.
Be cautious, most of these claims are unproven.
While it may not be possible to fully reverse nerve damage, especially if it stems from aging or chronic disease, many treatments can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Think of it like anti-aging cream: it can improve how your skin looks and feels, but it won’t make you look like a teenager again.
The same applies to nerves.
At-Home Treatment Strategies
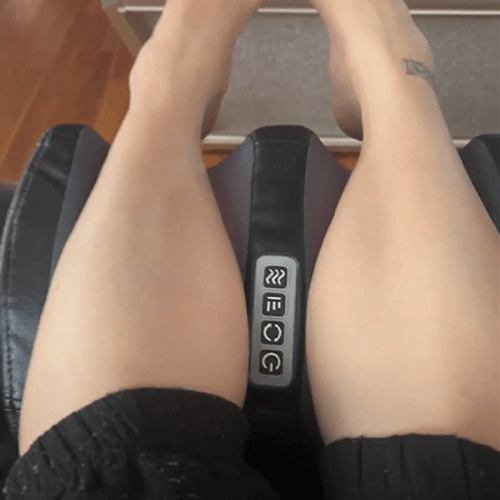
Massage & Icing
Massage can boost circulation and reduce discomfort.
Try rolling a rubber or plastic bottle (filled with cold water if tolerated) under your feet for 10–15 minutes.
Avoid extreme cold if you find it aggravates your symptoms.
Stretching & Flexibility
Stretching your calves, hamstrings, and feet can reduce tension and swelling.
Use a towel to gently pull your foot toward you, especially before bed and after waking.
Tools like slant boards can help you gradually increase flexibility.
Topical Relief
-
Cooling creams: These produce a cooling or warming effect that can distract the nerves and reduce pain.
-
Moisturizers and oils: Thick creams and essential oils (e.g., lavender, aloe vera, magnesium) can soothe dry skin and lessen irritation.
Movement & Circulation
Gentle walking or simple foot exercises can help reduce nighttime swelling and improve nerve function.
Elevating your feet and using compression socks may also help.
Supportive Footwear
Footwear plays a critical role in managing neuropathy. Unsupportive shoes can stretch and irritate nerves.
Look for shoes and slippers with firm arch support and cushioned soles.
Orthotic inserts can prevent the foot from flattening and keep nerves protected.
Even around the house, avoid walking barefoot.
Use supportive slippers or sandals to reduce strain on your feet.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Diet & Weight Management
Reducing blood sugar and body weight can greatly reduce neuropathy symptoms, particularly in people with diabetes.
Eat a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and avoid high-sugar and processed items.
Avoid Alcohol & Smoking
Alcohol and tobacco restrict blood flow and contribute to nerve damage.
Cutting back or quitting can lead to noticeable improvements.
Sleep & Recovery
Lack of sleep can raise pain sensitivity.
Aim for 7–9 hours of restful sleep per night to support nerve repair and reduce symptoms.
Key Takeaways
-
Peripheral neuropathy is often manageable with daily home care.
-
Massage and stretching can ease swelling and reduce nerve pressure.
-
Supportive footwear and orthotics are essential for protecting nerve health.
-
Topical treatments like cooling creams and moisturizing oils can offer short-term relief.
-
Managing health conditions (e.g., diabetes, thyroid issues) is critical.
-
Avoiding alcohol and smoking improves circulation and nerve function.
-
Quality sleep supports nerve recovery and reduces pain sensitivity.